
Walmart helps people worldwide save money and live better – anytime and anywhere – by providing the opportunity to shop in retail stores and through eCommerce and access its other service offerings.
Through innovation, Walmart strives to continuously improve a customer-centric experience that seamlessly integrates its eCommerce and retail stores in an omnichannel offering that saves time for the customers. Each week, Walmart serves approximately 230 million customers who visit more than 10,500 stores and numerous eCommerce websites under 46 banners in 24 countries.
Walmart’s business strategy is to make every day easier for busy families, operate with discipline, sharpen the culture and become more digital, and trust a competitive advantage.
Price leadership has been a cornerstone of Walmart’s business strategy and model. By leading on price, Walmart earns customers’ trust by providing a broad assortment of quality merchandise and services at everyday low prices (“EDLP”).
EDLP is Walmart’s pricing philosophy and business strategy under which it prices items at a low price daily, so customers trust that prices will not change under frequent promotional activity. Everyday low cost (“EDLC”) is Walmart’s commitment to control expenses so the cost savings can be passed to customers.
Let’s closely analyze the business model and supply chain strategy of Walmart.
Walmart has global operations of retail, wholesale and other units, as well as eCommerce, located throughout the U.S., Africa, Canada, Central America, Chile, China, India, and Mexico. The business model of Walmart makes money from three segments: Walmart U.S., Walmart International, and Sam’s Club. Walmart made $567.8 billion in fiscal 2022 through these three segments. Each component contributes to the Company’s operating results differently.
Walmart U.S. is the largest segment and operates in the U.S., including in all 50 states, Washington D.C. and Puerto Rico. Walmart U.S. is a mass merchandiser of consumer products, operating under the “Walmart” and “Walmart Neighborhood Market” brands and walmart.com and other eCommerce brands. Walmart U.S. had net sales of $393.2 billion for fiscal 2022, representing 69% of Walmart’s revenue in fiscal 2022.
Omni-channel: Walmart U.S. provides an omnichannel experience to customers, integrating retail stores and eCommerce through services such as pickup and delivery, ship-from-store, and digital pharmacy fulfillment options. As of January 2022, Walmart had approximately 4,600 pickup locations and more than 3,500 same-day delivery locations.
Walmart+ membership offers enhanced omnichannel shopping benefits that include unlimited free shipping on eligible items with no order minimum, unlimited delivery from the store, fuel and pharmacy discounts, and mobile scan & go for a streamlined in-store shopping experience.
Merchandise: Walmart U.S. does business in three strategic merchandise units, listed below:
The Walmart U.S. business also includes an in-house advertising offering via Walmart Connect, supply chain and fulfillment capabilities to online marketplace sellers via Walmart Fulfillment Services, and access to quality, affordable healthcare via Walmart Health.
In Fiscal 2022, Walmart’s U.S. initiatives also included the launch of a B2B last-mile delivery service platform via Walmart GoLocal, and Walmart Luminate, which provides a suite of data products to merchants and suppliers.
Additional service offerings include fuel, financial services, and related products (including through digital channels, stores, and clubs as well as its previously announced fintech joint venture), such as money orders, prepaid access, money transfers, check cashing, bill payment, and certain types of installment lending.
Distribution & supply chain strategy: Walmart U.S. has a total of 157 distribution facilities from which the majority of Walmart U.S.’s purchases of store merchandise are shipped. General and dry grocery merchandise are transported primarily through the segment’s private truck fleet. Walmart ships merchandise purchased through eCommerce platforms by many methods from multiple locations, including its 31 dedicated eCommerce fulfillment centers, or delivers directly from more than 3,500 stores.

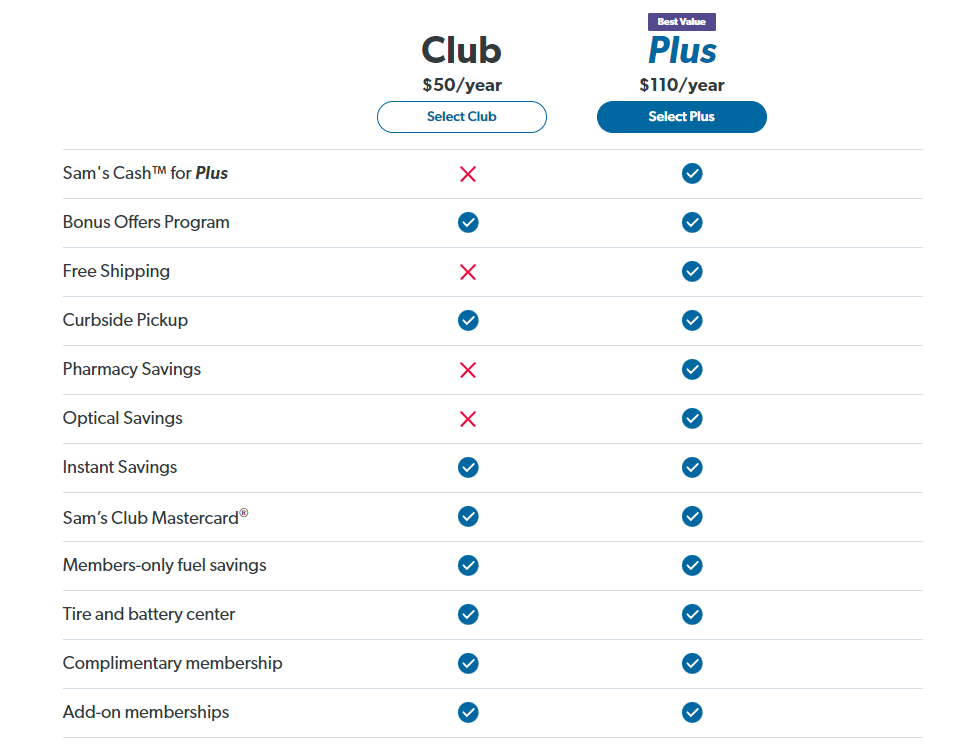
All memberships include a spouse/household card at no additional cost. Plus Members are also eligible for free shipping on most merchandise, with no minimum order size, and receive discounts on prescriptions and glasses. Members may redeem Sam’s Cash on purchases in the Club and online to pay for membership fees or cash in clubs.
Omni-channel: Sam’s Club provides an omnichannel experience to customers, integrating retail stores and eCommerce through such services as Curbside Pickup, mobile Scan & Go, ship-from-club, and delivery-from-club. The warehouse facility sizes generally range between 32,000 and 168,000 square feet, with an average size of approximately 134,000 square feet.
Merchandise: Sam’s Club offers merchandise in the following five merchandise categories:
Distribution & supply chain strategy: Walmart has 28 dedicated distribution facilities located strategically throughout the U.S. Some of the Walmart U.S. segment’s distribution facilities service the Sam’s Club segment for certain items. Most of Sam’s Club’s non-fuel club purchases are shipped from these facilities, while the remainder is shipped directly to Sam’s Club locations by suppliers.
Sam’s Club ships merchandise purchased on samsclub.com and through its mobile commerce applications by several methods, including shipments made directly from clubs, 12 dedicated eCommerce fulfillment centers, and other distribution centers. Sam’s Club uses a combination of Walmart’s private truck fleet and common carriers to transport non-perishable merchandise from distribution facilities to clubs.
As a retailer and warehouse club operator, Walmart utilizes a global supply chain strategy that includes U.S. and international suppliers from whom it purchases merchandise in its stores, clubs, and online.
In many instances, Walmart purchases merchandise from producers near the stores and clubs where such merchandise will be sold, particularly products in the “fresh” category. Walmart offers its suppliers the opportunity to sell significant quantities of their products to Walmart efficiently.
These relationships enable Walmart to obtain pricing that reflects the volume, certainty, and cost-effectiveness these arrangements provide to such suppliers, allowing it to offer low prices to customers.
Walmart’s ability to acquire from its suppliers the assortment and volume of products, to receive those products within the required time through its robust supply chain strategy, and to distribute those products to its stores and clubs, determines the attractiveness of Walmart’s merchandise assortment.
Walmart strongly focuses on building a sustainable supply chain in its business model.
To help address the effects of climate change, Walmart has set science-based targets for emissions reduction to achieve zero emissions in operations by 2040 —without offsets—and to reduce or avoid one billion metric tons of emissions in its value chain by 2030.