Database Testing Tutorial – Complete Beginners Guide
In this Database Testing guide, we will discuss everything you need to know about Database Testing.
What is meant by Database Testing?
Database testing checks the integrity and consistency of data by verifying the schema, tables, triggers, etc., of the application’s database that is being tested. In Database testing, we create complex queries to perform the load or stress test on the database and verify the database’s responsiveness.
An issue in the database might cause a crash or leakage of data, we are aware of the importance of keeping the privacy of the user’s data. So, it is crucial to perform database testing to ensure data integrity, consistency, etc., are being maintained.
By performing database testing we can guarantee the security and reliability of an application as it exposes the vulnerability in the database.
- 30+ Database Testing Interview Questions for Software Testers
- 20+ ETL Testing Interview Questions
- 100+ SQL Interview Questions
What are the benefits of Database Testing?
- Database testing helps in ensuring the database’s efficiency, stability, performance, and security.
- During database testing, we can understand the behavior of complex transactions and how the system handles such queries.
- It makes sure that only valid data values and information are received and stored in the database.
- Database testing protects us from vulnerabilities like data loss, saves aborted transaction data, and doesn’t allow access to information for unauthorized users.
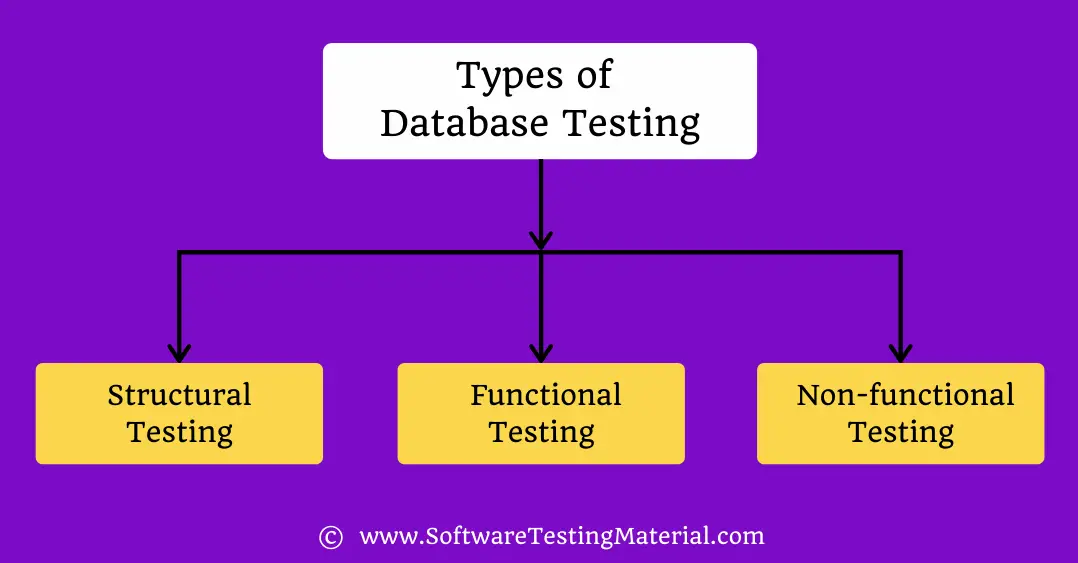
What are the different database testing types?
Based on the function and structure of a database, the database testing can be classified into the three categories listed below.
- Structural Testing
- Functional Testing
- Non-functional Testing
You should also ensure that your testing covers database activities like data integrity, data validity, triggers, and functions in the database.
#1. Structural Testing
- Structural database testing deals with testing components that are not accessible by the end-user.
- Structural testing validates the components in the data repository that is primarily used for storage, like table & column testing, stored procedures and views testing, checking triggers, etc.
- You should possess a good amount of knowledge in SQL queries to execute this testing.
Schema Testing
- Schema testing in databases ensures that the schema mapping is similar on both the back end and the front end of the application and validates various schema formats.
- The schema represents the logical view of the entire database, i.e. map of our database, thus it provides directions for the actual query process that allows us to fetch accurate data.
- Schema testing involves validating several schema formats that are associated with the databases and it also helps in finding the unmapped objects in a database, like tables, views, columns, etc.
- It also verifies the consistency of a heterogeneous database in an environment with the overall application mapping.
- Schema testing is also called mapping testing.
Database/Column Testing
- In Database/Column Testing, we will be validating the structure of the database, along with its feature column, and verify if they are consistent.
- It verifies the field lengths and naming conventions match on all levels of the application for both the back end and user interface of the system.
- It also checks whether any unused or unmapped tables and columns must be accounted for and validate their presence.
- It validates the efficiency and correctness of the summary view for the user interface by checking the data types and length of data in the back end of the application.
- It checks if the primary and foreign keys have their respective tables and whether they are set as per the domain standards.
- Even the not null or other unique characteristics should also be accounted for.
Trigger Testing
- Trigger testing validates the procedural flow of database code works and makes sure that it is free of bugs.
- It validates the functionalities such as update, inserts, deletes trigger functionality in the application.
- Checks, whether the trigger executed, meet the required condition.
- Verifies the data update when the trigger is executed.
- The tester has to make sure that the coding conventions are followed during the coding phase of the triggers.
Stored Procedure and View testing
- In this type of testing, it checks the coding standards, exception, and error handling for all the stored procedures.
- It makes sure that conditions, loops, and other functions are covered in the coding by applying the appropriate data in the application.
- It checks whether the TRIM operations are applied properly when the data is fetched from the corresponding tables in the database.
- It validates the overall integration of the stored procedure module according to the requirements.
- Verifies the error handling and exception procedures.
Table and Column Testing
- It checks the front end of the application’s field values for the data types in the database.
- It verifies the length of the data field to the length in the database of the data types in the application.
- It checks whether there are any unmapped tables or columns in the database.
- It verifies whether the naming conventions in the database tables and columns are according to business requirements.
- It checks the Keys and indexes (primary and foreign key) in the database as given as per requirement.
- It verifies the association between the primary key and the corresponding foreign key.
- It checks whether the characteristics of unique and NOT NULL keys are maintained.
- It validates the length and data type of the keys and indexes.
Database Server Validations
- It checks whether the server configuration of the database is as per the business requirement.
- It makes sure that the user can perform only certain levels of action that are required.
- It ensures that the database server can handle the maximum number of user transactions that are allowed based on the business requirement specifications.
Keys and Indexes Testing
- It checks the primary key and foreign key constraints on the database.
- It validates the foreign key references in the tables.
- It checks whether the keys and indexes are based on naming conventions.
- It verifies the size and length of the required fields.
- It makes sure that the clustered indexes and non-clustered indexes created in the required tables are as per business requirements.
#2. Functional Testing
Functional Testing focuses on the functionalities such as transactions and operations performed by the end-user in the application. It makes sure that these functionalities are as per business requirements.
Black Box Testing
- Black box testing in the database involves checking the data integrity and basic functionalities.
- Test Cases in this testing include verifying the incoming and outgoing data while performing the functions.
- This testing uses various techniques like boundary value analysis, equivalence partitioning, cause and effect graphing technique, etc to test the functionality in the database.
- Black box testing is comparatively simple and cost-effective which can be performed in the early stage of testing.
- The major drawback here would be, only a few errors can be found, and we don’t know how much should be tested.
White Box Testing
- White Box testing in the database focuses on the internal structure and the specification details that the user is unaware of.
- It deals with checking the database triggers and logical view which supports data refactoring.
- In this testing, database function, triggers, views, SQL queries, etc are verified by conducting module testing.
- It helps in validating database tables, data models, database schema, etc., even checks the rules of Referential integrity.
- It checks the database consistency of the application by selecting default table views.
- This testing uses various techniques like conditional coverage, decision coverage, statement coverage, etc. to validate the internal level coding of the database.
- The best part about white box testing is that it detects coding errors, this helps in eliminating internal bugs in the database.
- But white box testing does not cover SQL statements.
#3. Non-Functional Testing
Non- Functional Testing performs load testing, stress testing, checks minimum system requirements to meet the business specification, detects risks, and optimizes the performance of the database.
Load Testing
- Load testing validates the impact of the most running transaction in the database, it checks the performance impact of such transactions.
- It checks the response time for executing transitions for multiple users located remotely.
- It validates the time taken for fetching a specific record from the database.
Stress Testing
- Stress testing helps in identifying the breakpoint of the system.
- It finds out this breaking point by loading the application until the system fails.
- LoadRunner and WinRunner are commonly used for stress testing.
What are the factors to check during database testing?
The primary goal of database testing is to validate the data mapping, data integrity, accuracy of business rules, and transaction properties.
Data Mapping
It deals with the data that travels back and forth between the user interface and the back end of the application.
Database testing evaluates whether any action triggered in the front end is invoked in the backend successfully.
Data Integrity
It focuses on the consistency and accuracy of the data, if data is updated or modified in the database, it should be available in all forms and screens.
Database testing validates all processes, operations, and methods used to access, manage and update the database for CRUD operation (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete).
Accuracy of business rules
Complex Database leads to complex components such as stored procedures, triggers, rational constraints etc.
Database testing takes care of the accuracy of the business rules by creating appropriate SQL commands to check complex objects.
Transaction properties
Every transaction in the database should support ACID properties for a successful transaction.
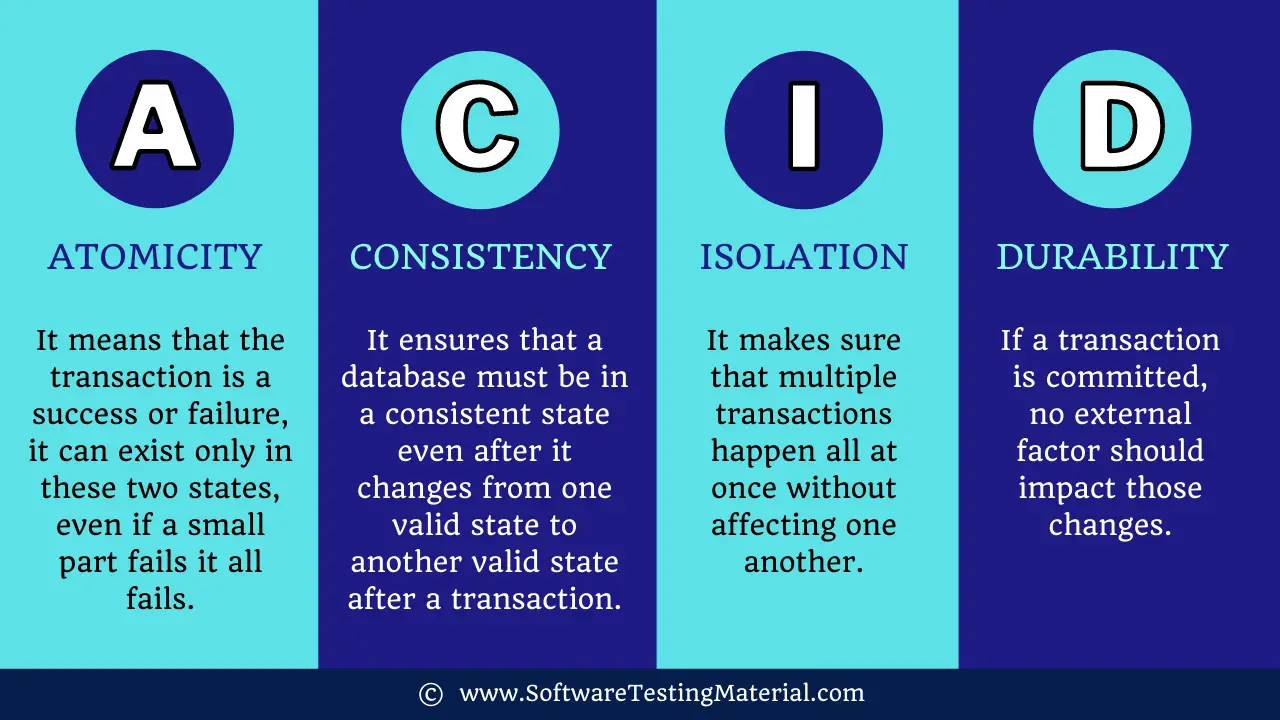
Atomicity: It means that the transaction is a success or failure, it can exist only in these two states, even if a small part fails it all fails.
Consistency: It ensures that a database must be in a consistent state even after it changes from one valid state to another valid state after a transaction.
Isolation: It makes sure that multiple transactions happen all at once without affecting one another.
Durability: If a transaction is committed, no external factor should impact those changes.
Database Schema
It is an abstract design that shows how the data is stored in the database, i.e., how the data is organized along with the relation associated with other data.
Transactions
A transaction is a small unit of a program that performs low-level tasks in the database.
Stored Procedure
It can be defined as a set of SQL statements that are stored and reused over and over again.
Field Constraints
It can be defined as rules used to limit the type of data that is being stored to maintain data integrity and consistency.
Triggers
It can be defined as stored programs that automatically execute when an event occurs.
How do you perform Database Testing?
The database testing process is similar to testing other applications. But we can use several tools and techniques to test our database, but these methods change depending on the applications, query, and other factors. Nonetheless, the basic steps to perform testing remain the same.
Step 1: Prepare the environment
Step 2: Execute the case
Step 3: Check the test results.
Step 4: Validate against the expected result.
Step 5: Report the results
While performing Database testing, we will be using various SQL statements. So having a strong grasp of SQL, DDL, DCL and DML is necessary to execute complex queries, in this context they would be the test case. Also, make sure that your test monitors the data mapping and ACID properties of the application.
- Open the SQL server in your local system.
- Open the Query Analyzer to write the command and retrieve the data.
- Compare the data that is retrieved with the expected results.
- You can either update or delete the data in the system to check how the application behaves under such circumstances.
- Here we can write complex queries to verify the expected output.
The tester should be well versed with SQL and database queries to perform database testing.
How do you write test cases for database testing?
Database testing is a type of grey-box testing as we have to verify the backend along with the user interface that fetches the data in the application. Most software applications have multiple databases, you have to understand how these are related to each other.
- Firstly, you have to understand the requirements of the application.
- Collect details on all the tables, whether they use joins, cursor, triggers, stored procedures, input and output parameters used.
- Start writing test cases for these tables, make sure that you have multiple input values to cover all the paths.
Sample Test cases:
- Verify whether the database name, device details, device log and dump device details, storage space can be displayed using queries.
- Verify if the details entered in the UI are saved in the database when the submit button is clicked in the application.
- Verify whether the primary key and foreign key are not accepting null values.
- Verify end-to-end data flow in the system, from front end to back end.
- Verify whether there is any deadlock, failure out of memory, data corruption, etc using the log files.
How can we automate database testing?
Database testing can be complex with an increase in data size, heterogeneous environment, and data complexity, it can be tiring to provide full coverage manually. For database testing, we can focus on key areas like data schema, data integrity, and basic user interface functionalities in automation.
- Identify what needs to be tested.
- Prepare Test Scripts
- Identify priority test cases.
- Run the test.
- Report the findings.
- Monitor the test results.
- Cross verify the results with UI test report
Which tools are used for database testing?
Some tools used for database testing:
- DataFactory
- MockupData
- DTM Data Generator
- MS SQL Server
- tSQL
- SQLite
- SQL Test
- Oracle SQL Developer
- NoSQLUnit
- SeLite
- SLOB
- Orion
What are the advantages of database testing?
- Database testing allows us to uncover bugs in the early phase of development, these issues might be very costly in the later stages of the development.
- It provides the system with higher test coverage.
- It helps in protecting the information of the user by checking scenarios to prevent unauthorized access, data leak, etc.
- It ensures the security and the quality of the software.
- It eases the complexity of the database backend so that the developers increase the use of View and Stored Procedures.
- It increases the robustness of the data by checking the data integrity and consistency regularly.
- It prevents deadlocks, data corruption, data leaks, etc.
What are the disadvantages of database testing?
- Database testing can be very complex when performed manually, the increase in data size, multiple relational databases, data complexity, etc can make it hard to test.
- Automation tools can increase the cost of the project.
- To perform database testing, the tester needs to have deep knowledge of the database, along with the functionality and requirements of the application associated with data.
- Changes in the database need to be constantly updated in the test plan.
- It can be difficult to identify the crucial items to be tested when the database is huge.
Real-time examples of database testing.
SQL queries used for database testing:
- To get the recent data from an employee database
SELECT TOP 1* FROM EMPLOYEE ORDER BY JOINING_DATE DESC
- To check for duplicate records
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE GROUP BY E_ID HAVING COUNT (*)>1.
- 30+ Database Testing Interview Questions And Answers
- JSON Schema Validation in Postman
- 100+ Types of Software Testing – The Ultimate List
- SQL Drop – SQL TUTORIAL | Software Testing Material
- SQL Create Database – SQL TUTORIAL | Software Testing Material




